Overview
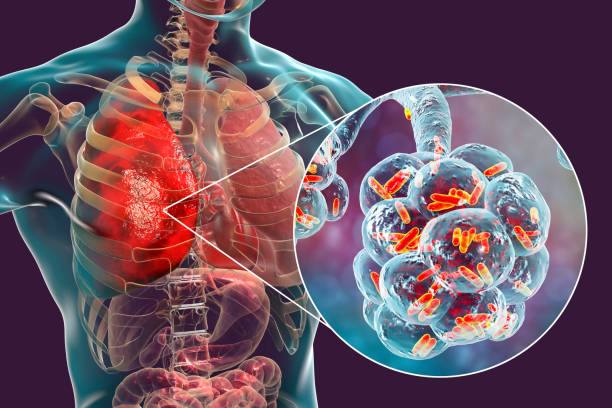
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection that most commonly affects the lungs and is caused by a specific type of bacteria. It spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or spit.
Tuberculosis is preventable and treatable.
It is estimated that about a quarter of the world’s population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Approximately 5-10% of people infected with tuberculosis eventually become symptomatic and develop tuberculosis disease.
If you are infected but have not (yet) become ill, you are not contagious. Tuberculosis is usually treated with antibiotics, but can be fatal if left untreated.
In some countries, bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine is given to infants and young children to prevent tuberculosis. The vaccine protects against tuberculosis outside the lungs, but not inside the lungs.
Important facts
In 2021, a total of 1.6 million people will die from tuberculosis (including 187,000 people living with HIV). Globally, tuberculosis is the 13th leading cause of death and the second leading cause of death from an infectious disease after COVID-19 (beyond HIV and AIDS).
In 2021, it is estimated that 10.6 million people worldwide will have tuberculosis (TB). 6 million men, 3.4 million women, 1.2 million children. Tuberculosis occurs in all countries and in all age groups. However, tuberculosis is both treatable and preventable.
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) remains a public health crisis and threat to health security, and in 2021, only one in three people with drug-resistant tuberculosis was receiving treatment.
Between 2000 and 2021, tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment saved an estimated 74 million lives.
Achieving the global goals agreed at the 2018 UN High-Level Conference on Tuberculosis will require $13 billion annually for tuberculosis prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care. Ending the tuberculosis epidemic by 2030 is one of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) health goals.
Symptoms
People with LTBI do not feel sick and are not contagious. Only a small percentage of people with tuberculosis develop tuberculosis and develop symptoms of tuberculosis. Babies and children are at higher risk.
Certain medical conditions can increase your risk of developing tuberculosis.
diabetes (hyperglycemia)
Weakened immune system (HIV, AIDS, etc.)
become malnourished
use of tobacco.
In contrast to tuberculosis infections, tuberculosis has symptoms. Because they cause mild symptoms for months, they can easily spread tuberculosis to others without knowing it.
Common symptoms of tuberculosis:
Persistent cough (sometimes with blood)
chest pain
weakness
Malaise
weight loss
heat
Night sweats.
The symptoms that develop depend on where tuberculosis is active in the body. Tuberculosis usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect the kidneys, brain, spine, and skin.